Microsoft Clarity’s Bot Activity Report shows how AI tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity access and interact with your website. It separates AI bot activity from human traffic so you can accurately understand your web analytics and improve your digital marketing decisions.
AI is changing how people discover and use websites. But it’s also changing your traffic data. Automated visits, AI crawlers, and assistant-driven requests are now mixed into your analytics alongside real human sessions.
If your traffic patterns look unusual lately, you’re not imagining it. AI systems are actively browsing, indexing, and querying your content — and most analytics platforms were built to measure activity, not identity.
That distinction matters.
Without separating bot activity from human behavior, you risk optimizing for signals that don’t reflect real audience interest.
Microsoft Clarity’s Bot Activity Report acts as a reality check. It helps you answer a critical question:
How much of my traffic is actually coming from people?
In this guide, you’ll learn where to find the report, how to interpret the data, and how to turn AI bot insights into better SEO, AEO, and GEO decisions.
How AI Bot Traffic Affects SEO and AEO Strategy
AI bot traffic changes how you should interpret performance metrics.
Bots can:
- Inflate pageviews
- Distort “top pages” reports
- Skew engagement metrics
- Trigger false conversion signals
A spike in crawl activity does not mean your rankings improved.
It does not mean your content was cited in an AI answer.
And it does not mean audience growth.
Crawlers are not citations.
However, bot activity is not inherently bad.
High AI crawl or assistant activity can signal that your content is being evaluated by generative engines. That may indicate an opportunity to refine your structure, clarity, and answer formatting for:
- AEO (Answer Engine Optimization) — optimizing for AI-generated answers
- GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) — strengthening your content for generative visibility and citation
If you mistake bot activity for human engagement, you may:
- Fix pages that aren’t broken
- Prioritize the wrong channels
- Misjudge content performance
- Celebrate or panic over misleading data
When analyzed correctly, AI bot traffic becomes directional insight instead of noise.
Microsoft Clarity’s new Bot Activity Report makes that separation visible, and without additional configuration.
Let’s look at how it the Bot Activity Report works.
Where to Find Microsoft Clarity’s Bot Activity Report
Microsoft Clarity is a free website analytics tool that helps you visualize user behavior. It makes it easy to understand what people read, skip, and click. It also provides visual heatmaps and anonymized session recordings. As of January 2026, it also shows something new: AI bot activity from sources like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, and more. Microsoft made things easy: you can view the report without any extra configuration.
- Confirm Microsoft Clarity is installed and tracking data. Go to clarity.microsoft.com, select the project for your website, and ensure there are existing recordings and heatmaps.
- Find the “Dashboards” menu item, click the dropdown, and select “AI Visibility”
Reviewing Microsoft Clarity’s Bot Activity Report
The dashboard for the Bot Activity report is broken down into three sections:
- Bot Operator
- Bot Activity
- Path Requests
Bot Operators
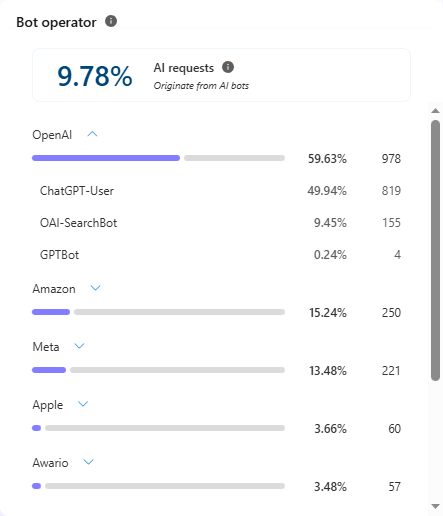
Bot Operators build, own, and operate AI tools. For example, OpenAI operates ChatGPT, Google operates Gemini, and Anthropic operates Claude. You may see one, a few, or all of these names in your report. Experts disagree on how many bot operators exist, from a dozen or so key players to hundreds of thousands of individual operators, but Forbes identified 50 to watch in April 2025.

The report automatically calculates what percentage of your requests it believes comes from AI bots and shows it at the top of the “Bot Operator” column. As of February 2026, almost 10% of Culture Foundry’s traffic can be attributed to bots. It then lists each operator in order of most visits to least visits. Expanding each operator provides a more detailed breakdown of what types of bots were used.
Bot Activity
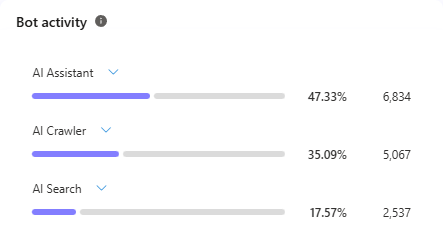
Bot Activity categorizes the type of task the bot is performing, and is broken down into three categories: AI Assistant, AI Crawler, and AI search. Think of AI Assistants as virtual versions of your visitors – they’re performing a task like collecting information, checking prices, or placing an order. AI Crawlers are automated bots that regularly visit pages to perform the same task, like checking for new blog posts or updating prices. AI Search activity refers to tools that are specifically looking to find contextual answers to questions. It is possible for all three types of tasks to be happening at the same time
The “Bot Activity” column lists the purpose of each visit in order of quantity. Expanding each activity gives you detailed information about which bot operator performed the activity.
Path Requests
Path Requests are the pages and sections of your site that bots are visiting.
The “Path Requests” column shows you where the bots went, and is sortable by the number of requests. You can export each of these columns as comma separated values (.CSV) files or as an image (.PNG). As the list of path requests is rather large, the complete list of data is only displayed if you scroll. If you want to be able to download all of the paths, you’ll need to scroll through the entire list. Otherwise your image or .csv file will be incomplete.
Limitations of Microsoft Clarity’s Bot Activity Report
Most AI bot reports only track known operators. Many automated tools do not announce who they are. Microsoft Clarity’s Bot Activity Report can only see bots that identify themselves. Other analytics tools have the same limit. They cannot monitor scrapers that hide their identity. This means the report shows declared AI traffic only. It does not show all visitors accessing your content.
Accuracy is another challenge. False positives can happen. Some crawlers may be misclassified. A crawl does not mean your content was cited. It only shows that a bot accessed the page. It does not prove the bot used your work in a response. The Microsoft Clarity Bot Activity Report report cannot confirm if you were cited. This is like Google Analytics: it cannot tell you if someone was emailed a link before clicking it on their phone.
There are also limits on historical data. The lookback window is short. This makes it hard to spot long-term trends or changes in AI activity. You cannot clearly measure patterns without deeper data. You cannot understand the bigger impact over time.
You can set a custom timeframe for Clarity’s Bot Activity Report. But Clarity only started collecting this data recently. For example, I tried to pull a report for Culture Foundry website visits in December 2025. The report found nothing.
How to Interpret the Microsoft Clarity Bot Activity Report
You can see what percentage of your traffic comes from known AI bots. This number appears at the top of the “Bot operator” column.
You can also see which operators your visitors use. This helps if you’re considering AEO (Answer Engine Optimization) or GEO (Generative Engine Optimization). You can decide which tool to optimize for first. For example, if Google is your #1 operator and you’re not optimizing for Gemini yet, you have a clear next step.
The bot activity data shows where you are in the AEO/GEO optimization process:
- High crawler activity means bots are just starting to notice and index your site
- High search activity means you’re likely appearing in AI overviews—tools are checking your site when they look for answers
- High AI assistant activity means your site powers virtual assistants, support bots, and “copilot”-like tools
Path requests show where AI bots spend the most time on your site. Look at your top pages. Find patterns in their content, purpose, or structure. Use these patterns to improve other pages. For example, if bots often visit pages with “how to” steps, try adding similar sections to other high-value pages. This may lead to more citations.
What to Do With What You Find
Add your bot operator percentage as a baseline to your regular web metrics. Monitor the percentage regularly. Check for changes both before and after you implement any optimization tactics.
If you notice unexpected spikes in traffic, impressions or other metrics, your bot activity may be a contributing factor. Use the data in the Bot Activity report to investigate your findings and compare your baseline metrics with suspicious activity. Don’t be afraid to cross-reference your Microsoft Clarity findings with those of another tool, like Google Analytics, HotJar, or your CDN’s dashboard.
Review your list of path requests for pages that should not be crawled. Are bots referencing an orphaned blog post with a typo in the URL and outdated information about a service you no longer offer? Do you see lots of bots crawling your /wp-admin/ folder? If you see pages you don’t want indexed, take a minute to update your robots.txt and llms.txt files to block access.
If you saw a number of AI operators you don’t recognize in your bot operator report, set aside some time to learn about them. Visitors to your site are using these tools. Understanding what they are, how they work, and why people are using them can help you better understand your prospects.
If you’re noticing a barrage of AI bot visits, work with your devops team to tighten rate limits, block particular operators altogether, or add simple protections to high-value forms.
Quick Reference: How to Interpret Your Bot Activity Report
| If this aspect is high: | Focus on this activity: |
|---|---|
| Crawler activity | Indexability and structure |
| AI search | Optimize for answer clarity |
| AI Assistants | Improve structured summaries and FAQs |
| Bot percentage spikes | Audit robots.txt and llms.txt |
Does Microsoft Clarity show if ChatGPT cited my site?
No. It shows bot visits, not citations.
Is AI bot traffic bad for SEO?
Not necessarily. It becomes a problem only if it distorts human engagement metrics
Should I block AI bots in robots.txt?
Only if they cause server strain or access outdated pages.
How often should I check the Bot Activity Report?
Monthly for trend tracking; weekly during traffic anomalies.
Conclusion
It can be jarring to discover massive changes in your web traffic patterns, but the numbers don’t always signal doom. Microsoft Clarity’s Bot Activity report can help you sanity-check the data coming from your web analytics tool. This way, you can ensure you’re providing the right content to both real users and AI bots. With the information in the report, you can interpret the new ways people – and computers – are using the information on your website.
Key Takeaways: Microsoft Clarity’s Bot Activity Report
- AI bots can significantly distort your analytics if not segmented.
- Microsoft Clarity’s Bot Activity report separates bot operators, activity types, and path requests.
- High crawler activity does not equal AI citations.
- Unexpected traffic spikes may be bot-driven, not user-driven.
- Regularly review robots.txt and llms.txt to control unwanted AI access.


